Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) are common, but in many cases can be avoided. Atherosclerosis and venous thrombosis are the two major manifestations of CVD. Both are caused by complex interactions of environmental and genetic parameters. An unhealthy lifestyle in combination with certain genetic variants can contribute to atherosclerosis. Relevant genes include those involved in endothelial dysfunction, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and inflammation. A combination of adverse influences (female hormone intake, immobilization, surgery or cancer) and variations in genes responsible for the coagulation system can also lead to thrombosis. Testing for genetic variations and adequate prophylaxis contributes to lower CVD risks.
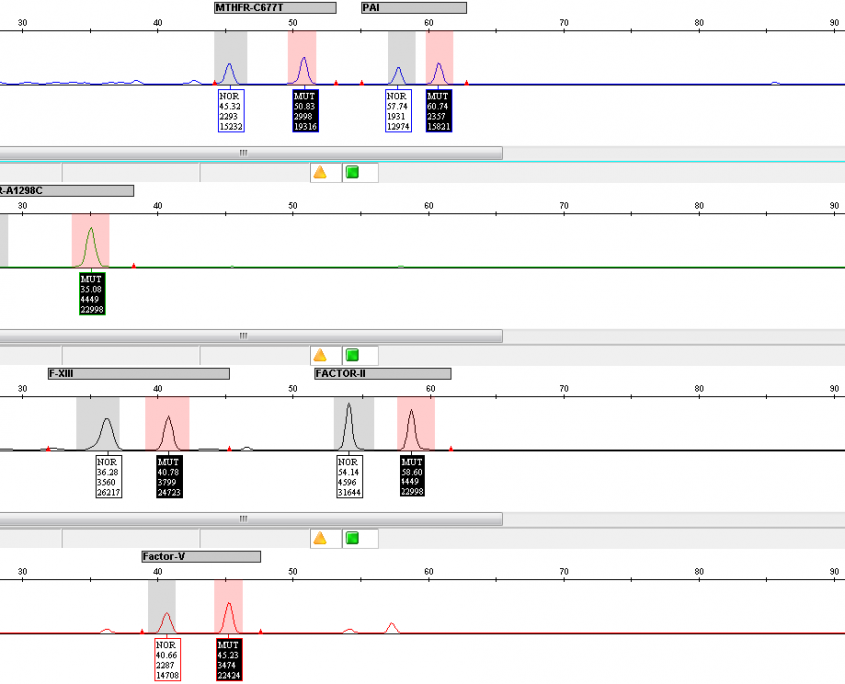
The system allows the detection and genotyping of a single point mutation of the human MTHFR gene at position c.677 (C to T) and c.1298 (A to C), Prothrombin (Factor II) gene at position 20210 (3′ untranslated region) (G to A), Factor V gene at position c.1691 (G>A, Leiden R506Q), FXIII (A1) gene at position codon 34 (G to T, V34L) and SERPINE1 (PAI1) at promoter site -675 (4G/5G) in the multiplex system containing six primer pairs for target amplification and twelve single-base-specific DNA probes for SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) detection. The kit which is intended for use on Applied Biosystems ABI PRISM® sequencers uses a five-dye fluorescent system allowing multiplex amplification/ligation in the same tube for automated SNP analysis.
- Incorporates an external control with a heterozygous pattern for all related mutations to ensure the performance and reliability.
- Using the same tube facilitates user’s hands-on time and circumvents possible cross-contamination
- Advances in capillary electrophoresis platforms and five-dye technology provide high precision and easy analysis.
- Precise and quick genotyping for all mutations in the same plot screen.
- Multiple samples can be analyzed in seconds, using GeneMapper® or GeneMarker Software.
- Wide range of DNA concentration (2 to 100ng/ml) and low DNA quality requirement (A260/A280 = 0.9 to 2.2) gives opportunity to use all type of specimens without DNA calculation and dilution.
- Minimal material and chemical consumption.
| Cat. No | Description |
|---|---|
| 208100.v.2.1 | 100 tests |
| 20850.v.2.1 | 50 tests |
| 20825.v.2.1 | 25 tests |
Please email us for product support requests and include your product LOT number.
Support e-mail: support@genomed-biotech.com